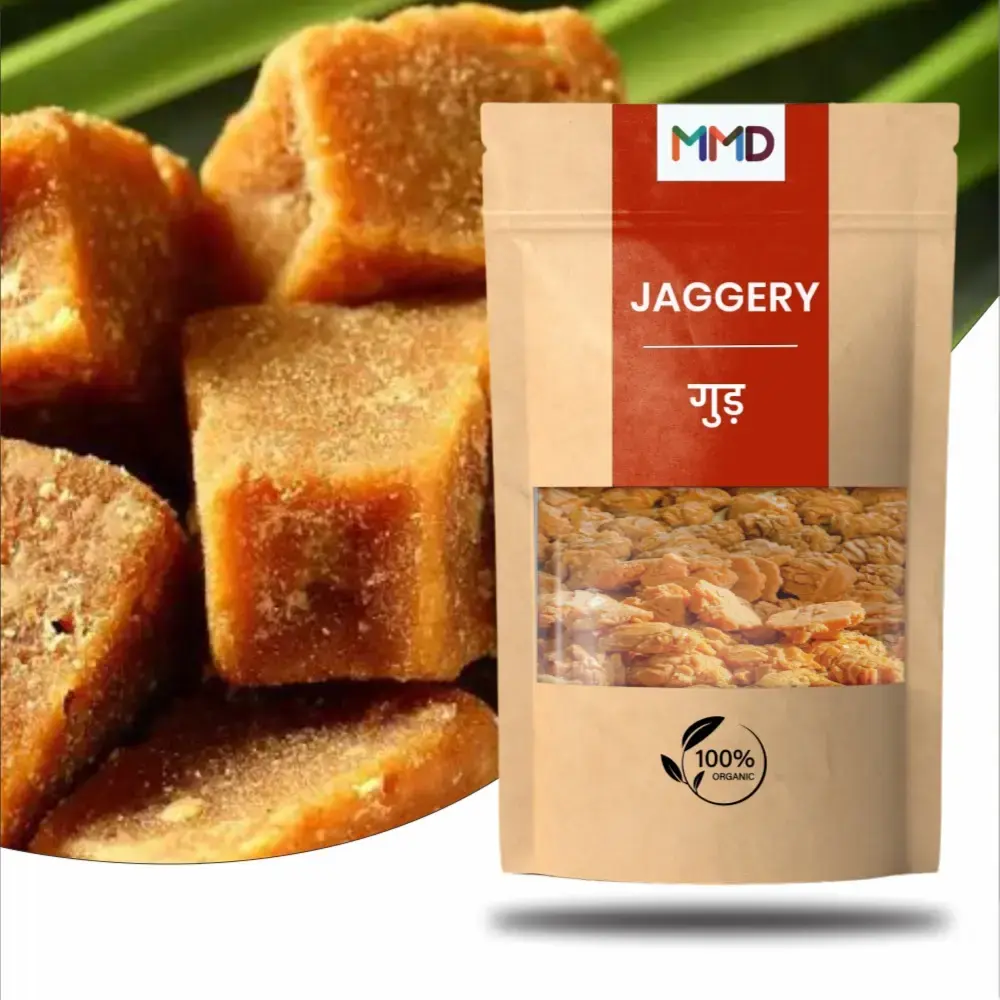
Jaggery, often referred to as "gur" in Hindi, is a natural sweetener that has been a staple in Indian cuisine for centuries. This unrefined sugar is derived from the sap of sugarcane or date palm trees and is revered for its rich flavor, distinct taste, and nutritional benefits.
The production of jaggery involves boiling sugarcane juice or date palm sap in large, shallow pans until it thickens and solidifies into a block or cake-like form. Unlike refined sugar, jaggery retains more of its natural molasses and minerals due to minimal processing, giving it its characteristic brown color and deep, caramel-like flavor profile.
The resulting jaggery possesses a complex sweetness with subtle hints of molasses and a rich, earthy aroma. It is commonly used as a sweetener in various Indian desserts, sweets, and beverages, imparting a unique depth of flavor to dishes like "gur wale chawal" (jaggery-infused rice), "gur ki roti" (jaggery-filled flatbread), or "gur ka halwa" (jaggery-based pudding).
Apart from its culinary uses, jaggery is valued for its perceived health benefits. It is considered a healthier alternative to refined sugar due to its relatively higher mineral content, including iron, calcium, and potassium. Additionally, it is believed to aid in digestion and is often used in traditional Ayurvedic medicine for various health remedies.
Jaggery is an integral part of Indian culture and cuisine, reflecting the country's rich heritage and diverse culinary traditions. Its natural sweetness, distinct flavor, and versatility make it an essential ingredient that adds depth and character to a wide array of savory and sweet preparations, while also offering potential health benefits. |